Adnexal Ectopic Pregnancy Pacs
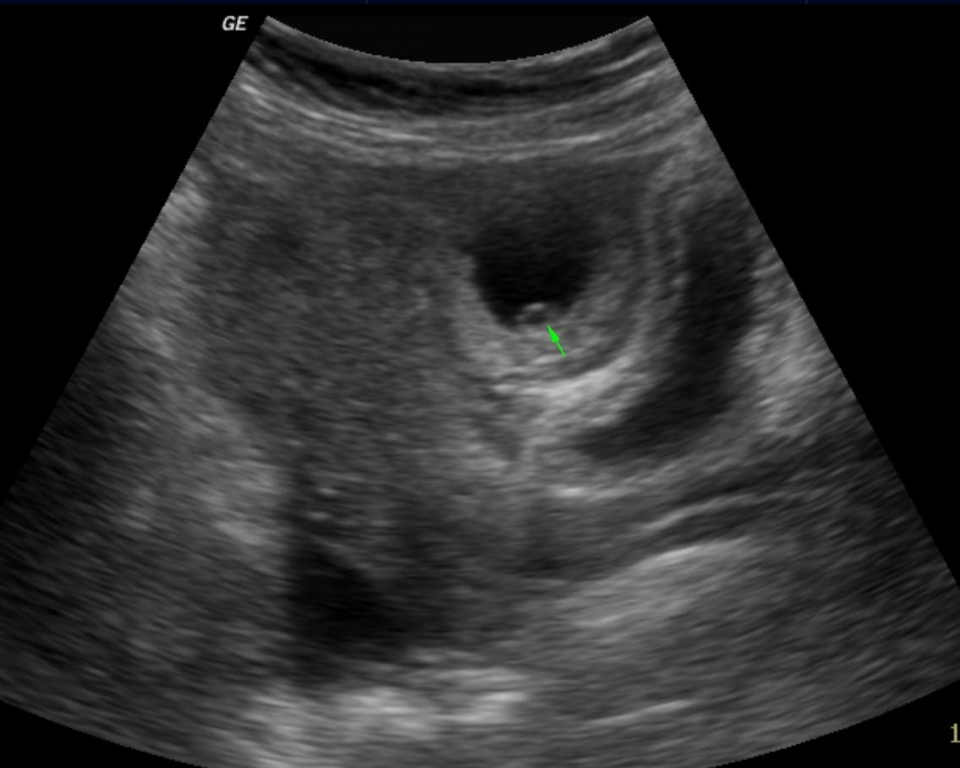
Adnexal Ectopic Pregnancy Pacs Tubal ectopic pregnancy (or adnexal ectopic pregnancy) is the most common location of an ectopic pregnancy. epidemiology. it is the most common type of ectopic by far, accounting for 93 97% of cases. pathology. although the fallopian tube has many anatomical parts, for the purposes of ectopic location it can be divided into : ampullary ectopic. Abstract. ectopic pregnancy is the implantation of a fertilized egg outside the uterine endometrial cavity. for women presenting to the emergency department with abdominal pain and or vaginal bleeding, ectopic pregnancy is an important diagnostic consideration. the diagnosis is made based on laboratory values and ultrasound imaging findings.
A Transvaginal Ultrasonography Of Left Adnexal Ectopic Pregnancy This guideline covers diagnosing and managing ectopic pregnancy and miscarriage in women with complications, such as pain and bleeding, in early pregnancy (that is, up to 13 completed weeks of pregnancy). it aims to improve how early pregnancy loss is diagnosed, and the support women are given, to limit the psychological impact of their loss. Ectopic pregnancy occurs when a fertilized ovum implants outside of the uterine cavity. the prevalence of ectopic pregnancy in the united states is estimated to be 1% to 2%, but this may be an. General complications for a typical (tubal) ectopic pregnancy include: tubal rupture: 15 20%. lithopedion: may result with larger ectopic pregnancies which have been left in situ. differential diagnosis. the differential diagnosis of abdominal pain in a pregnant patient is broad. an ectopic pregnancy must be excluded by ultrasound. Ectopic pregnancy accounts for approximately 2% of all pregnancies and is the most common cause of pregnancy related mortality in the first trimester. initial evaluation consists of hormonal assays and pelvic ultrasonography (us). a history of pelvic pain along with an abnormal β human chorionic gonadotropin level should trigger an evaluation for an ectopic pregnancy. the fallopian tube is.

Tubal Ectopic Pregnancy Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org General complications for a typical (tubal) ectopic pregnancy include: tubal rupture: 15 20%. lithopedion: may result with larger ectopic pregnancies which have been left in situ. differential diagnosis. the differential diagnosis of abdominal pain in a pregnant patient is broad. an ectopic pregnancy must be excluded by ultrasound. Ectopic pregnancy accounts for approximately 2% of all pregnancies and is the most common cause of pregnancy related mortality in the first trimester. initial evaluation consists of hormonal assays and pelvic ultrasonography (us). a history of pelvic pain along with an abnormal β human chorionic gonadotropin level should trigger an evaluation for an ectopic pregnancy. the fallopian tube is. Adnexal masses are identified in pregnant patients at a rate of 2 to 20 in 1000, approximately 2 to 20 times more frequently than in the age matched general population. the most common types of adnexal masses in pregnancy requiring surgical management are dermoid cysts (32%), endometriomas (15%), functional cysts (12%), serous cystadenomas (11%), and mucinous cystadenomas (8%). approximately 2. Postural symptoms. examination. adnexal tenderness and masses. state of cervix and material passing through it. fetal heart (almost never heard in ectopic) investigations. beta hcg (should almost double every 2 days) bloods to rule out other causes of abdominal pain. rh status.

Comments are closed.