A Learning Curve
The Learning Curve Theory Types Benefits Limitations 2023 Whatfix A learning curve is a graphical representation of the relationship between how proficient people are at a task and the amount of experience they have. proficiency (measured on the vertical axis) usually increases with increased experience (the horizontal axis), that is to say, the more someone, groups, companies or industries perform a task. The learning curve is the visual representation of the relationship between an individual’s proficiency in a task and their experience performing the task. there are many benefits for managers for understanding the learning curve, including being able to forecast breakeven points and costs and understanding the organization’s.
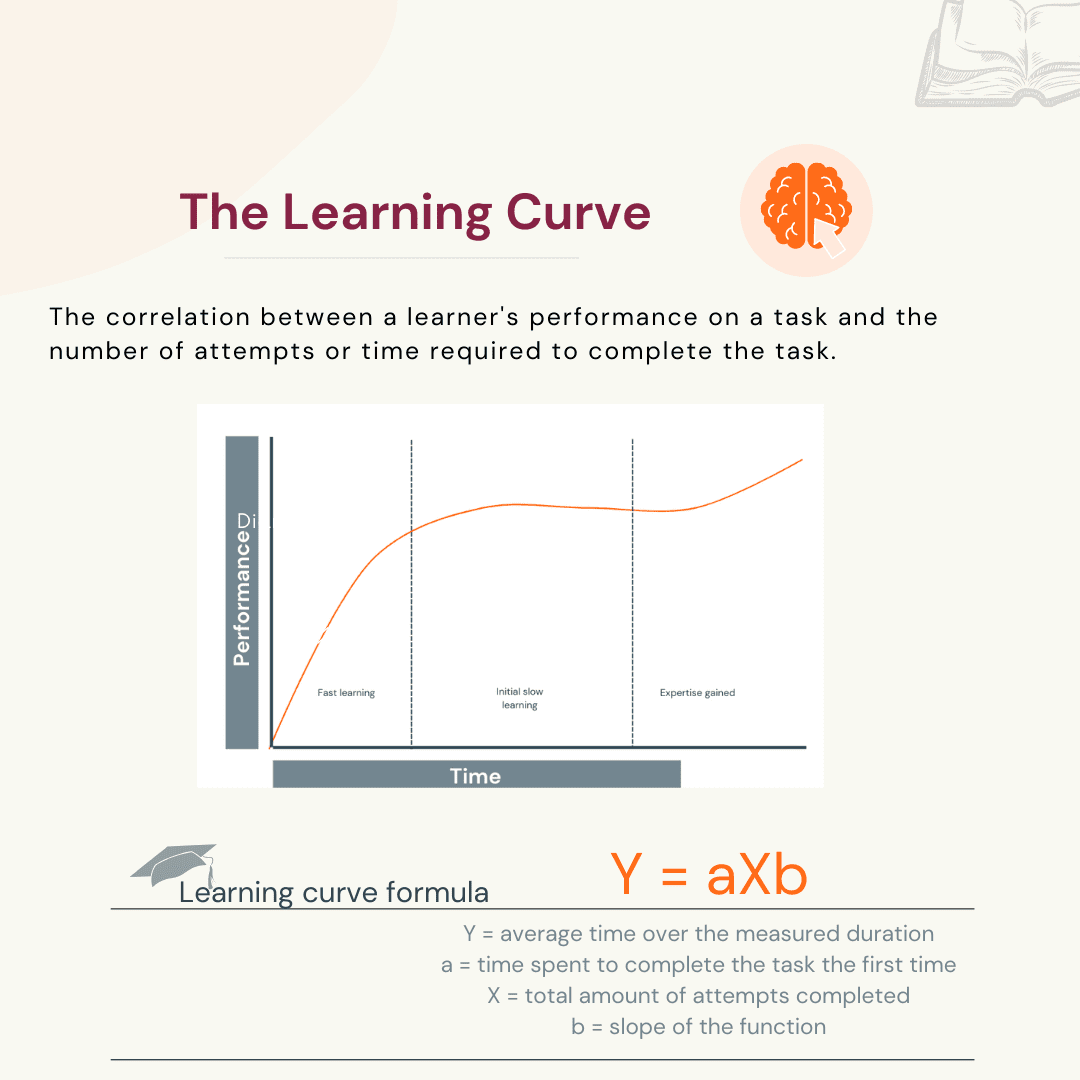
10 Tips To Improve Your Learning Curve And Achieve More Lifehack Learning curve formula. the original model uses the formula: y = axb. where: y is the average time over the measured duration. a represents the time to complete the task the first time. x represents the total amount of attempts completed. b represents the slope of the function. The learning curve is a visual representation of how long it takes to acquire new skills or knowledge. in business, the slope of the learning curve represents the rate in which learning new skills. The original learning curve theory formula is: y = ax^b. x = the total units of production or times task completed. the learning curve is the correlation between a learner’s performance on a task or activity and the number of attempts or time required to complete the activity. The learning curve is the relationship between a learner’s competency in completing a task and the time needed to become proficient in said task. this is represented by a simple line graph, which represents the five different competency stages. 📈. the theory proposes that a learner’s efficiency improves over time. practice makes perfect.
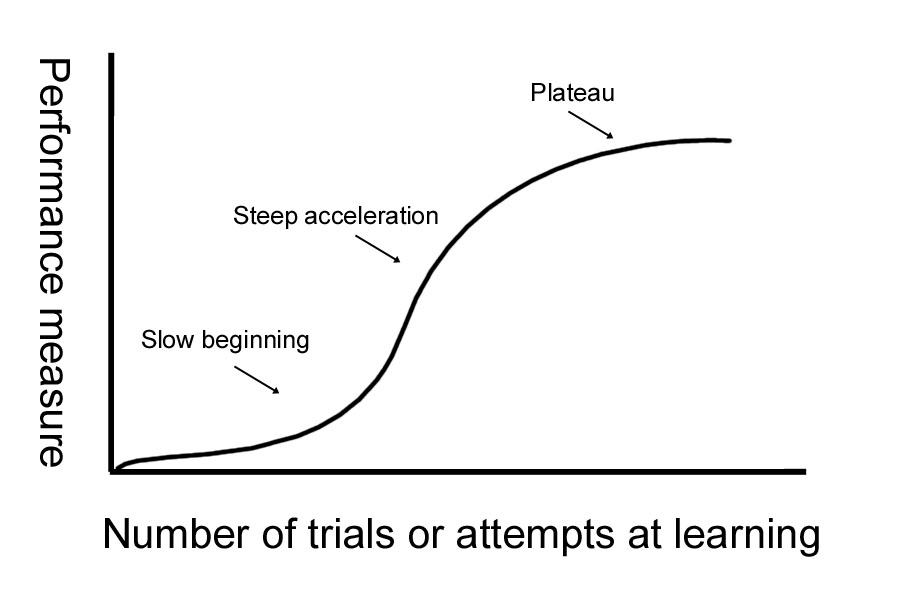
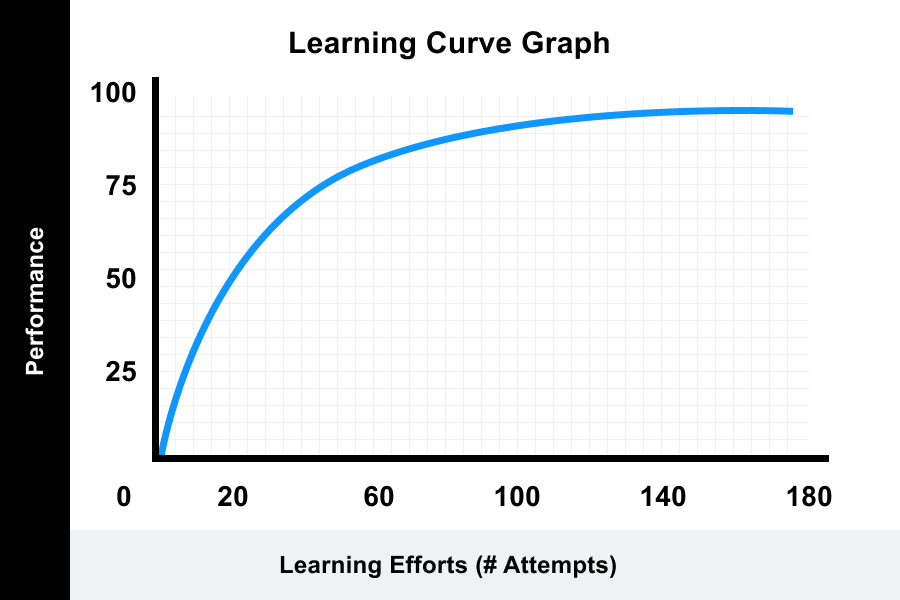
Learning Curve Definition Theory Graphs And Examples The original learning curve theory formula is: y = ax^b. x = the total units of production or times task completed. the learning curve is the correlation between a learner’s performance on a task or activity and the number of attempts or time required to complete the activity. The learning curve is the relationship between a learner’s competency in completing a task and the time needed to become proficient in said task. this is represented by a simple line graph, which represents the five different competency stages. 📈. the theory proposes that a learner’s efficiency improves over time. practice makes perfect. 1. diminishing returns learning curve. in the diminishing returns curve, you learn quickly when you begin, but as time goes on, the speed at which you learn slows down. in this learning curve, you start by making big strides in your learning. imagine a graph where your progress shoots up steeply. The origins of learning curves. learning curves were first described in research by aeronautical engineer t. p. wright in 1936. [1] he was studying how long it took to produce airplane parts. as workers gained experience, wright saw that they were able to produce the parts faster. efficiency improved – up to a point.

What Is The Learning Curve Explained In 2 Min Youtube 1. diminishing returns learning curve. in the diminishing returns curve, you learn quickly when you begin, but as time goes on, the speed at which you learn slows down. in this learning curve, you start by making big strides in your learning. imagine a graph where your progress shoots up steeply. The origins of learning curves. learning curves were first described in research by aeronautical engineer t. p. wright in 1936. [1] he was studying how long it took to produce airplane parts. as workers gained experience, wright saw that they were able to produce the parts faster. efficiency improved – up to a point.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/learning-curve.asp-final-443c359b1e644639beda742acd00f172.png)
What Is A Learning Curve Formula Calculation And Example

Comments are closed.