10 Important Ct Head Scans Neurology Radiology Ctscan

Approach To Ct Head Learningneurology Ct head, also known as ct brain, refers to a computed tomography (ct) examination of the brain and surrounding cranial structures. it is most commonly performed as a non contrast study, but the addition of a contrast enhanced phase is performed for some indications. this article covers non contrast and delayed post contrast imaging. Summary. a computed tomography (ct) head scan uses x rays to develop a 3d image of the skull, brain, and other related areas of the head. a ct scan of the head can provide more detail than a.

How To Read A Head Ct Scan Faculty Of Medicine During a brain ct, the x ray beam moves in a circle around the body, allowing many different views of the brain. the x ray information is sent to a computer that interprets the x ray data and displays it in a two dimensional (2d) form on a monitor. brain ct scans may be done with or without "contrast." contrast refers to a substance taken by. This tutorial takes you through the important anatomy required to understand ct images of the brain. tutorial orientation. ct images of the brain are conventionally viewed from below, as if looking up into the top of the head. this means that the right side of the brain is on the left side of the viewer. the anterior part of the head is at the. Computed tomography (ct) provides rapid, noninvasive imaging of the brain and skull. ct is superior to magnetic resonance imaging (mri) in visualizing fine bone detail in (but not the contents of) the posterior fossa, base of the skull, and spinal canal. A ct scan, or computed tomography scan, is a non invasive medical test that helps physicians diagnose and treat medical conditions. by combining a series of x ray views taken from different angles, the ct scan provides a comprehensive image of the internal structures of the head. this detailed imaging is crucial for evaluating the brain, skull.
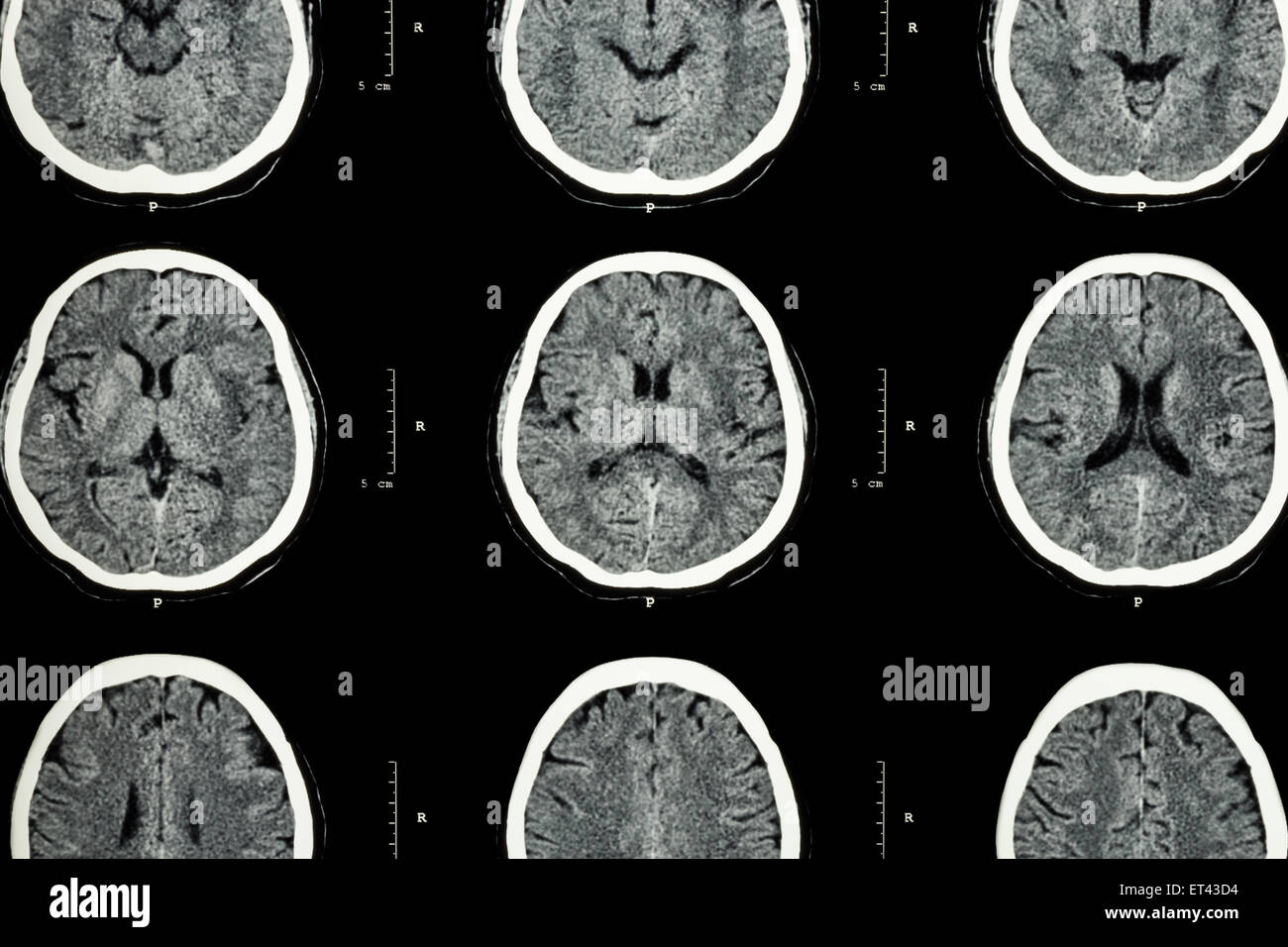
Normal Head Ct Scan Computed tomography (ct) provides rapid, noninvasive imaging of the brain and skull. ct is superior to magnetic resonance imaging (mri) in visualizing fine bone detail in (but not the contents of) the posterior fossa, base of the skull, and spinal canal. A ct scan, or computed tomography scan, is a non invasive medical test that helps physicians diagnose and treat medical conditions. by combining a series of x ray views taken from different angles, the ct scan provides a comprehensive image of the internal structures of the head. this detailed imaging is crucial for evaluating the brain, skull. In 1971, the first computed tomography (ct) scan was performed on a patient’s brain. clinical ct systems were introduced in 1974 and dedicated to head imaging only. new technological developments, broader availability, and the clinical success of ct led to a steady growth in examination numbers. most frequent indications for non contrast ct (ncct) of the head include the assessment of. After head trauma, a ct scan can reveal skull fractures. the scan can help locate even small fractures that may lead to serious health concerns. additionally, a ct scan can show bleeding, nerve or tissue damage or assess the severity of the condition following a known skull fracture. 8. multiple sclerosis.

Ct Head Open Med School In 1971, the first computed tomography (ct) scan was performed on a patient’s brain. clinical ct systems were introduced in 1974 and dedicated to head imaging only. new technological developments, broader availability, and the clinical success of ct led to a steady growth in examination numbers. most frequent indications for non contrast ct (ncct) of the head include the assessment of. After head trauma, a ct scan can reveal skull fractures. the scan can help locate even small fractures that may lead to serious health concerns. additionally, a ct scan can show bleeding, nerve or tissue damage or assess the severity of the condition following a known skull fracture. 8. multiple sclerosis.

Comments are closed.